OSI Model - 1
Open system Interconnection
(OSI) Model - 1
Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model :-
Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model was developed by the International Standards Organization (ISO) describes the flow of information from one computer to another. OSI model is also called ISO OSI Reference Model. It is conceptual model that has seven layers. Physical, Data link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation and Application are the seven layers of OSI model. Each layer performs distinct functions on the data in accordance with the precious layer functions. The application, presentation and session layers are called as Upper layers.
 |
| 7 layers of OSI model |
All the layers of the OSI reference model use different protocols. Protocol defines the procedure that is to be followed during data transmission. It is the set of specified rules and standards used to transmit data from one device to another.
(1.1) Physical layer :-
Physical layer is the first or the bottom most layer of the OSI model. This layer is used to establish or terminate a connection to a communication medium. It also defines the electrical and mechanical specifications like cables, connectors and signalling options of the medium.
Physical layer receives data from the upper layer called the data link layer. It Converts the received data into bit stream. The data is then transmitted through the medium to the receiver. At the receiver end, physical layer receives the data in to the bit format. It forwards the data to the data link layer. The functioning of the Physical layer is shown in the figure below :
 |
| Physical Layer |
- Characteristics of media : Defines the characteristics of the interface which is used for connecting devices. It also defines the type of transmission media such as copper wires of fibre optic cables.
- Encoding : Defines the encoding type. Encoding means changing bit stream (0s and 3s) into signal. Before transmission physical layer encodes the signal into electrical or optical form depending upon the media.
- Transmission Rate : Defines the transmission rate of bits. This provides number of bits transmitted per second. It defines how long will the duration of bit be.
- Transmission Mode : Defines the Transmission mode between two devices. Transmission mode specifies the direction of signal flow. The different types of transmission modes are : (1) Simplex, (2) Half duplex, (3) Full duplex.
- Topology : Defines how devices are connected to form a network.
(1.2) Data link layer :-
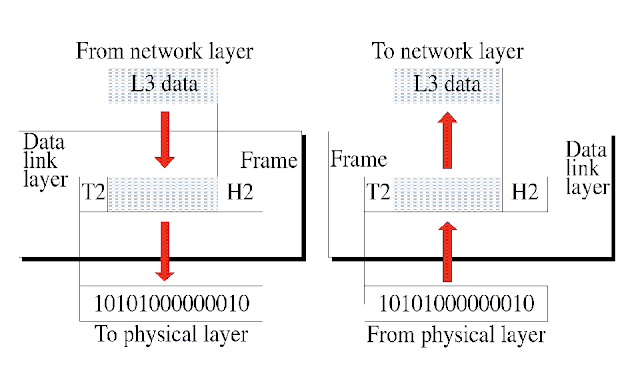
Data Link Layer is second layer of the OSI model. It handles data transfer between network and the physical layers. Data unit at the data link layer is called as Fame. Functioning of data link layer is shown in the figure:
 |
| Physical Layer |
Data a link layer receives the Data from the network layer. It adds Header and Trailer of the data and passes data to the physical layer. At the receiver side, Data link layer receivers data from the physical layer. It detaches Header and trailer from the data and passes Data to network layer.
Responsibilities of the Data link layer are :
- Framing : The Physical layer delivers raw bits from the source to destination. During Transmission, the value of the bits can change. It is also possible that the number of bits receive by the receiver may be different from the number of bits sent by the sender. To resolve this problem, the data link layer organizes the bit into manageable data units called as frames.
- Physical addressing : Data link layer adds Header to the frame which contain the physical address of the sender and/or receiver. Headers are assigned when the frames are to be distributed to various system within the network.
- Error Control : Another function of the data link layer is error control. Error control detects and corrects errors. During Transmission, if a frame is lost or corrupted, the data link layer re-transmits that frame. It also prevents duplication of frames. Error control is accomplished using Trailer at the end of the frame.
=================================================
Thanks for reading !
Have a GOOD DAY !



Nice Tutorial bro
ReplyDeletegod and Interesting
ReplyDeleteAwesome bro.. You explained this very easily
ReplyDelete